Baf 2 is less soluble than lif but relatively more soluble than mgf 2 and caf 2.
Barium fluoride optical windows.
Barium fluoride baf is a crystalline compound of barium and fluoride used in optical applications in the nir vis and mwir spectrums.
Thorlabs barium fluoride baf 2 precision windows are available in ø1 2 and ø1 sizes.
An ar coating maximizes the transmission over 3 to 5 µm r avg 2.
Barium fluoride baf2 is the fastest known scintillator material and barium fluoride windows and plates are used in vuv and infrared spectroscopy.
Baf 2 is recommended for use as a vacuum ultraviolet window where high radiation resistance is required.
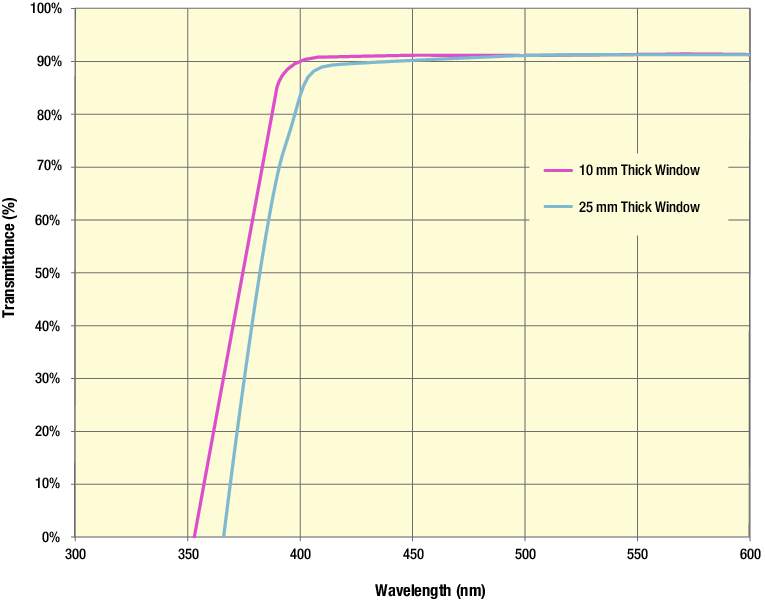
Although these windows are ar coated on both sides for ir use barium fluoride is commonly chosen for applications that require transmission into the ultraviolet.
Barium fluoride windows can be used up to 800 c in a dry environment but prolonged exposure to moisture can degrade transmission in the vacuum ultraviolet range.
For an equivalent thickness the transmission extends approximately 1 micron further into the ir than calcium fluoride.
Barium fluoride baf2 windows.
Barium fluoride baf is also a scintillation material that exhibits one of the fastest known decay constants among inorganic materials.
Barium fluoride is often suitable for applications in the passive ir band 8 to 14 μm and is often used as a viewport window for thermography.
Barium fluoride is used for optical windows prisms and lenses transmitting from ultraviolet into infrared it can be used as an infrared laser window or lens.
Barium fluoride baf2 lenses windows mirrors filters and prisms.
Barium fluoride is resistant to high energy radiation performing well in dry temperatures up to 800 c but transmission in the vacuum uv vuv degrades over time in a moist atmosphere and the material is susceptible to water corrosion at 500 c.
Used for optical windows prisms and lenses transmitting from the vacuum ultraviolet into the infrared.